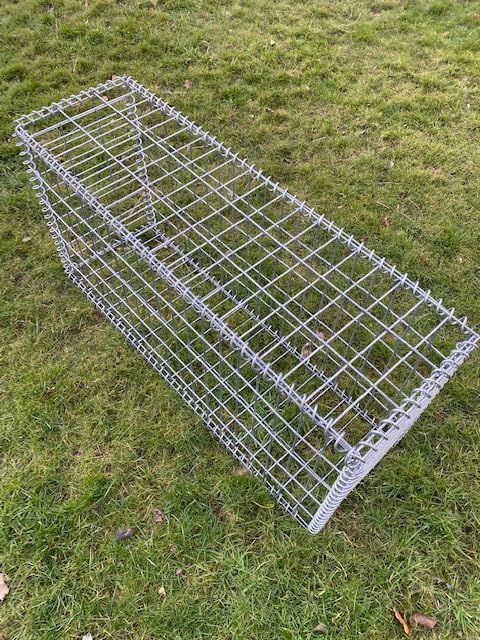
Introduction to Gabions
Gabions are structural containers made of wire mesh, typically filled with natural stones, aggregates, or soil, commonly used in civil engineering, landscaping, and environmental applications. These versatile structures serve various purposes, such as erosion control, retaining walls, and decorative features in gardens. In addition to their structural advantages, gabions provide ecological benefits by facilitating vegetation growth, which can stabilize surrounding soil and enhance biodiversity.
The construction of gabions employs materials of varying types and qualities, with galvanised wire being a predominant choice. Galvanisation involves coating steel wire with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion, boosting the longevity and durability of the gabion structures. This protective layer allows gabions to withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for riverbanks and coastal areas where exposure to moisture and saline environments can otherwise lead to deterioration.
Historically, the use of gabions can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where they were employed for fortifications and flood control. Over the centuries, these wire mesh containers evolved from simple baskets filled with rocks to highly engineered solutions in modern construction. Today’s gabions are designed to meet specific engineering requirements and often feature advanced materials that enhance their performance. The resurgence of interest in sustainable construction practices has furthered gabion usage, as they offer a low-impact solution for creating embankments and barriers while respecting the natural landscape.
In summary, gabions represent a creative and functional approach to civil engineering and landscaping. Their construction techniques, particularly the use of galvanised wire, contribute significantly to their effectiveness and durability, making them a popular choice for various applications across different sectors.
The Benefits of Galvanised Wire for Gabion Construction
Galvanised wire offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred option for gabion construction. One of the most significant benefits is its enhanced durability, as the galvanisation process provides a protective coating that improves resistance to environmental factors. This added layer of zinc shielding prevents corrosion, ensuring that the wire maintains its integrity over extended periods, thus prolonging the overall lifespan of the gabions. Such longevity is particularly advantageous in applications exposed to moisture and other harsh conditions, such as erosion control and flood protection.
Another critical benefit of using galvanised wire in gabion units is its exceptional strength. Galvanised wire is known for its robust mechanical properties, which allow gabions to support considerable weight and resist the pressures of soil and rocks. This makes it an ideal choice for stabilising slopes and creating solid structures. Furthermore, the flexibility of galvanised wire contributes to its versatility in design, enabling engineers and landscape architects to create intricate structures that align with the specific requirements of a project.
Ease of installation is another important advantage associated with galvanised wire gabions. The availability of various wire thicknesses provides multiple options suited for different applications, and this versatility simplifies the construction process. The lightweight nature of the galvanised wire also allows for less labor-intensive handling and assembly, making it easier to transport and install at the site. As a result, projects can be completed more efficiently and cost-effectively, which is especially beneficial in both large-scale and smaller undertakings where time and budget considerations are essential.
In summary, the benefits of using galvanised wire for gabion construction include its durability against corrosion, strength for reliable support, flexibility for versatile design possibilities, and ease of installation. These attributes contribute to why galvanised wire is a favored material in various applications, enhancing the effectiveness and longevity of gabions in diverse environments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Galvanised Wire Gabions
Constructing galvanised wire gabions can be a rewarding project, providing functional and aesthetic benefits for landscaping or erosion control. To begin the process, you will need to gather specific tools and materials. Essential tools include wire cutters, pliers, gloves, and a level, while the main materials consist of galvanised wire mesh, stones or gravel, and anchors if necessary for stability.
Start by planning the layout of your gabion. Determine the size and shape you wish to achieve; this will guide the selection of the galvanised wire mesh dimensions. Once you have a clear plan, proceed to cut the wire mesh according to your specified measurements, ensuring each piece aligns with your design. Assemble the gabion frame by bending the mesh into the required shape, using pliers to secure corners and joints. It is advisable to wear gloves during this step to protect your hands from sharp edges.
Next, fill the assembled wire mesh with stones or gravel. When committing to this step, choose stones that are suitably sized for the mesh openings; this will enhance the structural integrity of the gabion. Carefully place the stones within the structure, ensuring that they are evenly distributed to maintain balance. If your gabion is particularly large, it may be beneficial to fill it in layers, allowing for better weight distribution.
Finally, secure the structure by fastening it into the ground using anchors, if required. This will help prevent movement or displacement over time. It is crucial to adhere to safety precautions throughout the construction process. Common pitfalls to avoid include not aligning the mesh properly or overfilling the gabion, which can lead to structural weaknesses. By following these guidelines, you can successfully construct robust and visually appealing galvanised wire gabions.
Maintaining & Troubleshooting Gabion Structures
Maintaining gabion structures constructed from galvanised wire is essential for ensuring longevity and effectiveness. Ongoing maintenance helps preserve not only the structural integrity but also the aesthetic appeal of these installations. Regular inspection routines are vital. It is advisable to conduct checks at least twice a year, particularly after significant weather events, to assess the condition of the gabions. During these inspections, look for signs of wire corrosion, which can weaken the overall structure. Any rust found should be treated promptly with rust-inhibiting solutions and re-coated as necessary.
Cleaning the gabion structures is another critical aspect of maintenance. Over time, debris, soil, and plant growth can accumulate within the wire containers. To maintain functionality and appearance, gently remove any obstructions. A soft brush or high-pressure water spray can be effective for this purpose without causing damage to the galvanised wire. Ensuring that the stones within the gabions are visible and unobstructed will enhance the visual aesthetics as well as prevent any waterlogging, which can lead to further complications.
Identifying potential issues before they escalate is key. Common problems include displacements in the structure, settling of stones, and visible gaps forming due to erosion. Addressing minor displacements can often involve repositioning the stones. For more severe issues, such as settling due to inadequate drainage, additional measures may need to be taken, possibly involving the re-evaluation of the site’s design. Implementing these troubleshooting tips and maintaining a regular care schedule can effectively prolong the life of galvanised gabion structures. Doing so will ensure they not only serve their intended purpose but also continue to enhance the environment in which they are installed.
Contact information — Please use contact form on http://www.abshot.com/contact/